How to Describe Injury Using Anatomical Terms
Note presence of foreign material in or around the wound. UPDATED to correct inferiorposterior error in original.
Anatomical Terminology Anatomical Basis Of Injury
Start studying Anatomical TerminologyTypes of Injuries.
. Just as maps are normally oriented with north at the top the standard body map or anatomical position is that of the body standing upright with the feet at shoulder width and parallel toes forwardThe upper limbs are held out to each side and the palms of the hands. To clearly state the area of injury the nurse uses the term sural which means the posterior surface of the lower leg rather than writing back area of the lower leg. They help to avoid any ambiguity that can arise when describing the location of structures.
Areas of significant adiposity can develop deep wounds. Describe the sensation. Undermining and tunneling may occur.
How would an emt use correct anatomical terms to describe the injuriespain and their location to the physician at the emergency room for jennie fell off her motorcycle and tore a nerve in her axillary region. The median plane which divides the body into left and right. Is something else going on.
A full thickness wound due to blunt trauma resulting in splitting of the skin. This is a space for friendly local discussions. In general when describing a fracture the body is assumed to be in the anatomic position and the injury is then described in terms of the distal component displacement in relation to the proximal component.
There may be tissue strands bridging the wound. Displacement can include one or more of. By using precise anatomical terminology we eliminate ambiguity.
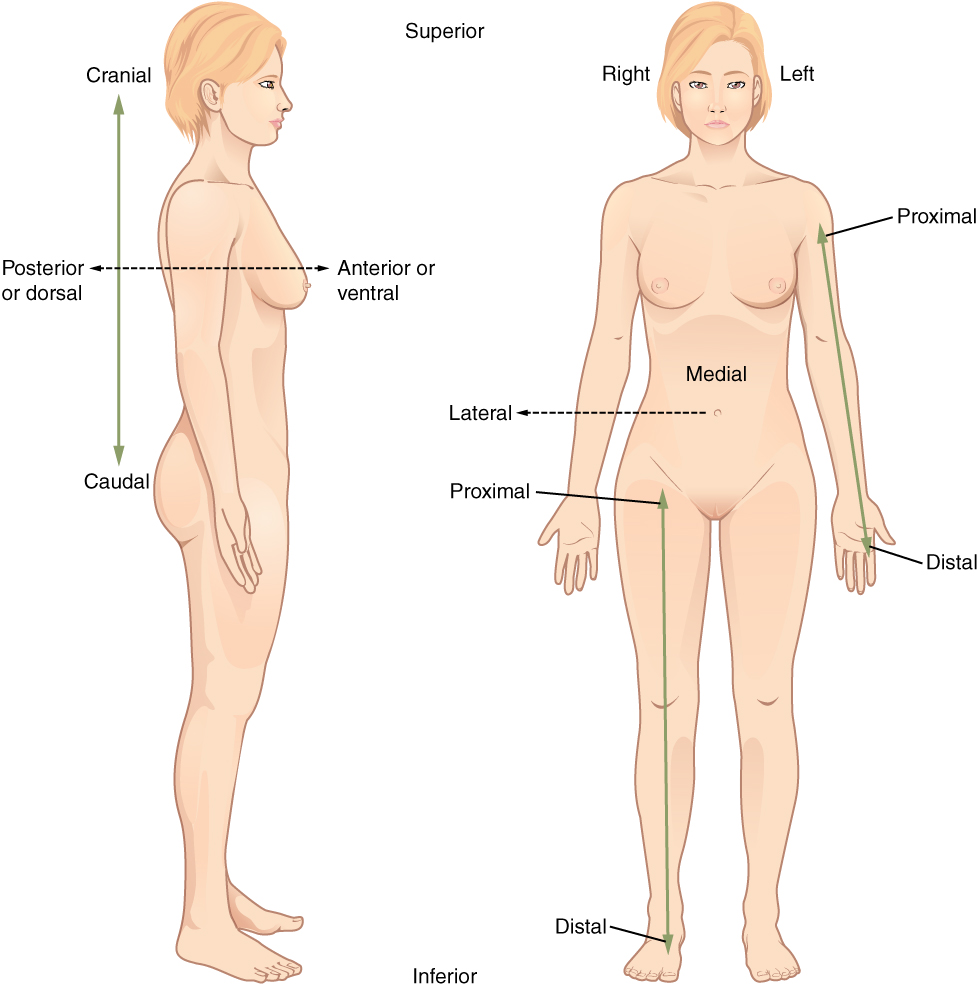
Anatomical terms are derived from ancient Greek and Latin words. Anatomical Directional Terms. The skin usually tears on impact where it overlies a relatively firm surface such as a bony prominence.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. The Anatomy of a Car Crash and The Injuries that Result. The wound edges may be ragged abraded bruised inverted.
Dimensions of wound should be measured. Anatomists and health care providers use medical terminology that can difficult and esoteric. Near the upper surface toward the back.
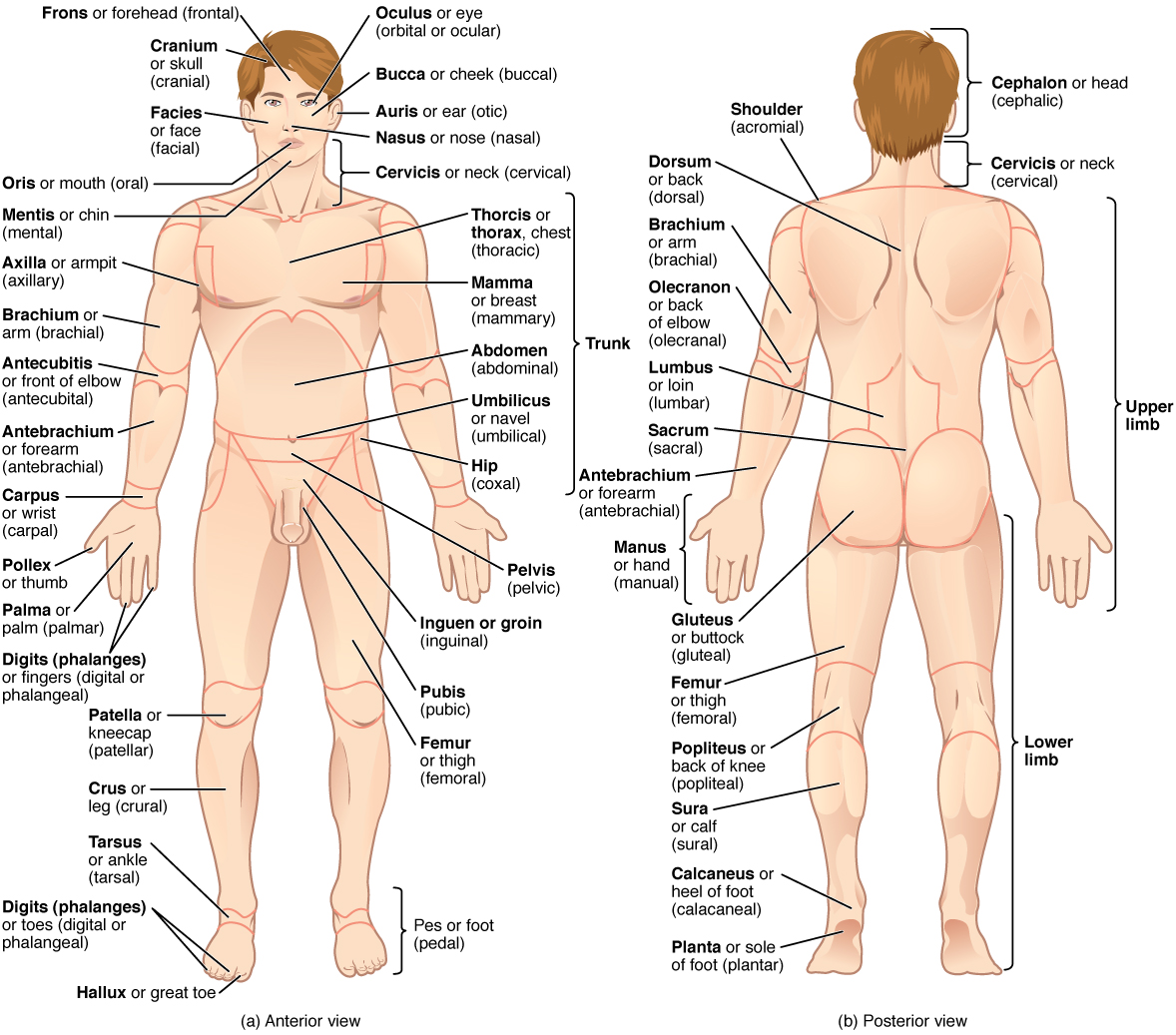
She also tore ligaments in her cervical and scapular regions and broke the only bone of her right brachial region. For example you might say a scar on the anterior antebrachium 3 inches proximal to the carpus. Away from farther from the origin.
In front of front. If slough or eschar obscures the extent of tissue loss this is an Unstageable Pressure Injury. To further increase precision anatomists standardize the way in which they view the body.
Fascia muscle tendon ligament cartilage andor bone are not exposed. Similarly femur or thigh is correct and leg or crus is reserved for the portion of the lower limb between the knee and the ankle. Learning these terms can seem a bit like a foreign language to.
Anterior or ventral - front example the kneecap is. Must identify all movements that occur in the upper body and the plane of motion in which the movements occur. The rules of replying.
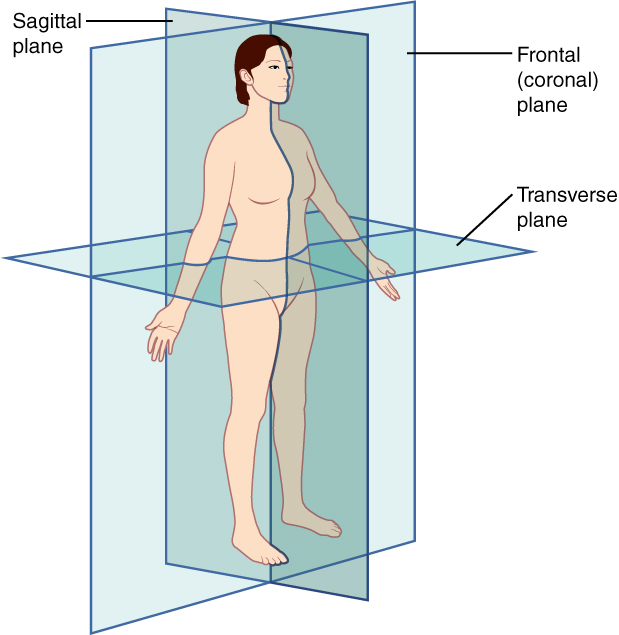
Lower example the foot is part of the inferior extremity. Condition of nearby tissues. The frontal plane also called the coronal plane which divides the body into front and back.
For example is an injury above the wrist located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand or at the base of the hand. This passes through the head spinal cord navel and in many animals the tail. The sagittal planes which are parallel to the median plane.
Anatomical position directional terms and body planes and sections - drawn defined and discussed. Toward the bottom toward the belly. Varies by anatomical location.
Near closer to the origin. You must use at least five anatomical descriptions to construct your narrative. Knowing these terms not only give the nurse a more accurate formulation of chief complaints but it also saves time of a good deal of description.
After behind following toward the rear. No racist discriminatory vulgar or. Anatomy and Physiology Describe an upper body movement or injury by using anatomical terms to describe the movement and musculature involved.
Upper example the hand is part of the superior extremity. Particularly when describing bruises. Anatomical terms describe structures with relation to four main anatomical planes.
Notice that the term brachium or arm is reserved for the upper arm and antebrachium or forearm is used rather than lower arm. Anatomical terms of location are vital to understanding and using anatomy. However the purpose of this language is to increase accuracy and reduce the chance for medical errors.
A description of an injury will include the site size shape orientation margins and wound type of the injury. Superior or cranial - toward the head end of the body. Inferior or caudal - away from the head.
The pain is a dull ache that throbs and goes away and then comes back or my lower back is like knot of burning pain like a huge muscle cramp in an area about 6-inches in diameter and it radiates into both buttocks and then goes down the right leg all of the way to my foot. Note any characteristics of the edges of the wound.

Anatomical Terminology Anatomical Basis Of Injury
Comments
Post a Comment